Contextualizing Scarcity and Intelligence in AI The current landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) encapsulates a paradox where computational power and model size are often mistaken as direct indicators of intelligence. In a world where colossal models are lauded for their billions of parameters, the fundamental principle of efficiency risks being overlooked. Historical examples, such as interstellar spacecraft and the human brain, illustrate that effective intelligence does not stem from sheer size but rather from optimizing limited resources. This notion posits that scarcity should not be perceived merely as a limitation, but as a catalyst for innovation and advancement in AI. The Main Goal: Efficiency Over Size The crux of the original discussion advocates for a paradigm shift in AI development, emphasizing that true intelligence manifests through efficiency rather than scale. This goal can be realized by prioritizing the design of compact, effective models that maximize performance while minimizing resource consumption. As we navigate through the complexities of AI, the emphasis should be placed on how to derive greater value from limited inputs, thereby fostering a culture of innovation that thrives within constraints. Structured Advantages of Efficiency in AI Cost-Effectiveness: Smaller, specialized models can achieve substantial functional value at a reduced cost compared to their larger counterparts. For instance, deploying a model with a trillion parameters for a specific task can be likened to using a supercomputer for basic calculations, illustrating the inefficiency of overkill. Reduced Latency: Models designed for edge inference can process data locally, diminishing the delays associated with remote data access. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications requiring real-time responses. Enhanced Privacy: By conducting inference on-device, sensitive information remains local, mitigating the risks associated with data transmission to cloud servers. Lower Environmental Impact: As AI systems increasingly require extensive energy resources, efficient models can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with large-scale data centers. Resilience and Adaptability: Systems that thrive within resource constraints demonstrate greater resilience, enabling them to adapt to varying environmental conditions and operational demands. However, it is important to note that while transitioning to smaller models offers clear advantages, potential limitations exist. For example, certain complex tasks may still require more extensive models to achieve desired accuracy levels, leading to a careful balance that must be maintained between size and performance. Future Implications for AI Development As the field of AI continues to evolve, the focus on efficiency over size is expected to gain momentum. The rise of technologies such as TinyML and edge AI signifies a shift towards localized solutions that can operate independently of expansive infrastructure. This trend not only democratizes access to AI capabilities in resource-limited environments but also aligns with the global push for sustainable and energy-efficient practices. Future developments in AI are likely to emphasize architectures that prioritize efficiency, ultimately reshaping the landscape of machine learning and its applications across various sectors. Conclusion The evolution of artificial intelligence is increasingly characterized by a commitment to efficiency as a measure of intelligence. By embracing the constraints of scarcity, practitioners can innovate and refine their approaches to machine learning, leading to sustainable and effective AI solutions. The future of AI will not be dictated by the magnitude of data or models but by the ingenuity to extract more from less, ensuring that intelligence is defined by its capacity for effective problem-solving in a resource-conscious manner. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here
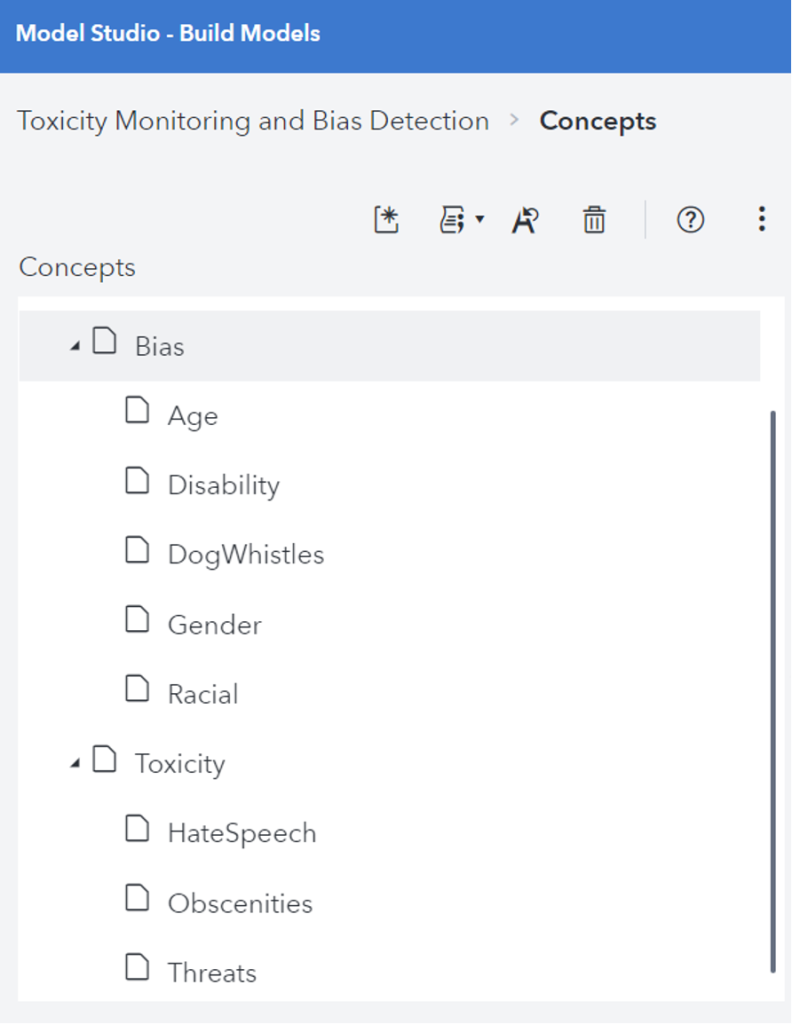
Introduction In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced the field of artificial intelligence, particularly in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and understanding. These models, trained on vast datasets, enable machines to produce human-like text responses. However, their deployment raises critical concerns regarding toxicity, bias, and exploitation by malicious entities. It is imperative for organizations utilizing LLMs to navigate these challenges to ensure ethical and effective AI solutions. Understanding Toxicity and Bias in LLMs The capabilities of LLMs are accompanied by inherent risks, notably the inadvertent perpetuation of toxic and biased content. Toxicity encompasses the generation of harmful or abusive language, while bias refers to the reinforcement of stereotypes and prejudices. Such issues can result in discriminatory outputs that adversely affect individuals and communities. Addressing these challenges is essential for fostering trust and reliability in AI-driven applications. Main Goal and Achievement Strategies The primary goal outlined in the original post is to manage toxicity and bias within LLM outputs to ensure trustworthy and equitable interactions. Achieving this involves a multifaceted approach that includes: Data Transparency: Organizations must prioritize transparency regarding the datasets used for training LLMs. Understanding the training data’s composition aids in identifying potential biases and toxic language. Content Moderation Tools: Employing advanced content moderation APIs and tools can help mitigate the effects of toxicity and bias. For instance, utilizing technologies like SAS’s LITI can enhance the identification and prefiltering of problematic content. Human Oversight: Continuous human involvement is crucial to monitor and review outputs, ensuring that new types of harmful content are recognized and addressed promptly. Advantages of Addressing Toxicity and Bias Addressing toxicity and bias in LLMs presents several advantages: Enhanced User Trust: By reducing instances of harmful language, organizations can foster a more trusted relationship with users, ultimately leading to greater user adoption and satisfaction. Improved Data Quality: Implementing robust monitoring and prefiltering systems enhances the overall quality of data fed into LLMs, resulting in more accurate and relevant outputs. Adaptability to Unique Concerns: Organizations can tailor content moderation strategies to address specific issues pertinent to their operations, allowing for nuanced handling of language-related challenges. Despite these advantages, challenges persist, particularly regarding the dynamic nature of language and the emergence of new harmful trends over time. Continuous adaptation and enhancement of moderation systems are crucial to overcoming these obstacles. Future Implications of AI Developments As AI technology continues to evolve, the implications for managing toxicity and bias in LLMs are profound. Future developments may include: Refined Algorithms: Advances in machine learning may lead to more sophisticated algorithms capable of detecting subtle biases and toxic language, enhancing the efficacy of content moderation. Greater Emphasis on Ethical AI: There will likely be an increasing focus on ethical AI practices, driving organizations to adopt more responsible approaches to AI deployment, particularly in sensitive applications. Legislative and Regulatory Frameworks: Governments may introduce stricter regulations governing the use of AI technologies, necessitating that organizations comply with enhanced standards for managing bias and toxicity. Ultimately, the future of LLMs hinges on the commitment of organizations to develop and implement responsible AI practices that prioritize ethical considerations while leveraging the transformative capabilities of these models. Conclusion In summary, the integration of LLMs into various applications necessitates a vigilant approach to managing toxicity, bias, and the potential for manipulation by bad actors. By prioritizing data transparency, employing effective content moderation tools, and ensuring continuous human oversight, organizations can cultivate a safer and more equitable AI landscape. The ongoing evolution of AI technologies underscores the need for responsible practices that benefit society while minimizing harm. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context and Importance of Prompt Injection in Large Language Models Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Claude are designed to interpret and execute user instructions. However, this functionality presents a significant vulnerability: the phenomenon of prompt injection. This technique allows malicious actors to embed covert commands within standard user input, effectively manipulating the model’s behavior. This manipulation poses risks analogous to SQL injection attacks in database systems, leading to potentially harmful or misleading outputs. Understanding prompt injection and its implications is crucial for ensuring the security and reliability of AI systems, particularly in the data analytics sector. Defining Prompt Injection Prompt injection refers to the manipulation of AI systems by embedding misleading commands within user inputs. Attackers can disguise harmful instructions as innocuous text, leading the AI to execute unintended actions. This vulnerability arises from the LLMs’ inherent inability to differentiate between trusted system commands and untrusted user inputs, making them susceptible to exploitation. Main Goal of Addressing Prompt Injection Risks The primary objective of addressing prompt injection is to safeguard AI models from unauthorized manipulation, which can lead to data breaches, safety violations, and the dissemination of misleading information. By implementing robust measures to detect and mitigate prompt injections, organizations can enhance the integrity and reliability of their AI systems. This involves a comprehensive approach that includes input validation, structured prompt design, and output monitoring. Advantages of Mitigating Prompt Injection Risks Enhanced Data Security: Effective input sanitization can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information, thereby protecting user data and organizational integrity. Improved Model Behavior: By controlling the prompts that the model executes, organizations can maintain alignment with intended use cases, minimizing the risk of harmful outputs. Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Proactively addressing prompt injection can help organizations adhere to privacy laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal repercussions. Increased User Trust: When users are assured that AI systems are secure and reliable, their confidence in utilizing these technologies grows, fostering wider adoption. Adaptive Learning Opportunities: Continuous monitoring and testing can provide insights into model vulnerabilities, enabling iterative improvements in system design. Despite these advantages, it is essential to note that complete eradication of prompt injection risks is unattainable. Organizations must remain vigilant, as attackers continually evolve their tactics. Future Implications of AI Developments in Prompt Injection The future of AI development emphasizes the need for increasingly robust defenses against prompt injection as LLMs become more prevalent across various industries. The integration of advanced monitoring systems and machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection could provide enhanced resilience against these threats. Moreover, as AI applications expand into critical sectors, including healthcare and finance, ensuring the integrity of these systems will become paramount. Continuous investment in research and development, as well as collaboration across the tech industry, will be necessary to address the evolving landscape of prompt injection attacks effectively. Conclusion Prompt injection represents a significant challenge in the deployment of large language models, threatening the security and functionality of AI systems. While it is impossible to eliminate all risks associated with prompt injection, organizations can substantially mitigate these threats through a combination of proactive measures, ongoing vigilance, and adaptive strategies. As AI technologies continue to advance, prioritizing the security of these systems will be essential for fostering trust and ensuring their safe application in diverse fields. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Contextual Overview of the Low-Power Computer Vision Challenge 2026 The Low-Power Computer Vision Challenge (LPCV) has emerged as a significant event within the Computer Vision and Image Processing domain, fostering innovation and collaboration among industry professionals and academic researchers. This year, the LPCV features three distinct tracks, namely Image-to-Text Retrieval, Action Recognition in Video, and AI-Generated Images Detection. Each of these tracks offers substantial financial incentives, with over $10,000 in prizes designed to motivate participants and encourage advancements in low-power computing methodologies. The LPCV not only serves as a platform for competition but also acts as a catalyst for discussions and knowledge exchange among experts in the field. The challenge is set to take place on January 29th, 2026, featuring notable guests such as Yung-Hsiang Lu, a Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, who will provide insights into the event’s objectives and significance. This initiative aligns with the overarching goals of enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of computer vision algorithms, which is crucial for various applications ranging from smart devices to autonomous systems. Main Goals of the LPCV and Achievement Strategies The primary goal of the LPCV is to stimulate innovation in low-power computer vision applications. This objective can be achieved through several strategies: 1. **Encouraging Participation**: By offering substantial prize money and recognition, the challenge motivates participants from diverse backgrounds to engage in the competition. This creates a rich environment for idea exchange and interdisciplinary collaboration. 2. **Fostering Research and Development**: The LPCV provides a structured framework for participants to test and refine their algorithms under competitive conditions, thereby pushing the boundaries of current capabilities in low-power computer vision. 3. **Promoting Real-World Applications**: Each competition track is designed to address real-world challenges, thereby ensuring that the research conducted is not only theoretical but also practical and applicable in industry settings. Through these strategies, the LPCV aims to catalyze advancements in computer vision technology that are not only innovative but also sustainable in terms of power consumption. Advantages of Participating in the LPCV Engagement in the LPCV offers several advantages for both individual participants and the broader field of computer vision: – **Financial Incentives**: With over $30,000 in prize money available, participants have a clear financial motivation to develop and showcase their innovative solutions. – **Visibility and Recognition**: Participants gain visibility within the research community, which can lead to future collaborations, funding opportunities, and career advancements. – **Skill Development**: Involvement in the challenge allows participants to hone their skills in algorithm design, testing, and real-time application deployment, which are invaluable in the rapidly evolving tech landscape. – **Networking Opportunities**: The LPCV serves as a gathering point for professionals in the field, facilitating networking and knowledge sharing that can lead to future partnerships and projects. Despite these advantages, some caveats exist, including the potential for high competition levels, which may deter newcomers, and the necessity for participants to have a solid foundational understanding of computer vision principles. Future Implications of AI Developments in Low-Power Computer Vision The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and low-power computer vision is poised to transform various industries, particularly as AI technologies continue to advance. Future implications include: – **Enhanced Algorithm Efficiency**: As AI techniques evolve, they will enable the development of more efficient algorithms that can operate on low-power devices without sacrificing performance, thereby broadening the applicability of computer vision technologies. – **Increased Adoption of Smart Devices**: With improvements in low-power computer vision, smart devices will become more capable, leading to increased adoption across sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and smart home technologies. – **Sustainability Focus**: As environmental concerns grow, the demand for energy-efficient solutions will drive innovation in low-power computer vision, aligning technological advancement with sustainability goals. In conclusion, the LPCV represents a vital opportunity for the advancement of low-power computer vision technology, fostering a competitive yet collaborative environment that is essential for addressing contemporary challenges in the field. As AI continues to develop, its integration with low-power computer vision will undoubtedly yield transformative impacts across various applications, ultimately shaping the future of this critical area of research. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context and Importance of Unified Metadata in Data Engineering In the evolving landscape of data engineering, the integration of various platforms for effective data management is critical. As organizations endeavor to leverage data for analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) applications, the challenges they encounter often extend beyond mere coding issues. Data engineers, analysts, and scientists require a coherent understanding of data lineage, transformations, and operational expectations. This necessitates a unified approach to metadata management that encapsulates business context, technical metadata, and governance across diverse platforms such as Alation and Amazon SageMaker Unified Studio. When metadata is siloed within different teams or systems, inefficiencies arise, leading to duplicated efforts and conflicting definitions. A unified metadata foundation is essential for ensuring that data remains trustworthy, accessible, and actionable across various analytics and AI initiatives. The recent integration between Alation and Amazon SageMaker Unified Studio aims to address these challenges by synchronizing catalog metadata. This synchronization fosters collaboration between technical and business teams, allowing them to work with the same metadata, thereby enhancing data traceability and understanding across the data lifecycle. Main Goal and Its Achievement The primary objective of the Alation and Amazon SageMaker Unified Studio integration is to establish a unified metadata governance framework that enhances data discoverability, governance, and compliance. Achieving this goal involves the automatic synchronization of metadata between the two platforms, which allows for a centralized view of assets and their associated information. This integration provides clear provenance, allowing organizations to track data origins and ensure regulatory compliance effectively. By leveraging this integration, organizations can streamline their data workflows, reduce metadata duplication, and foster a more collaborative environment for data professionals. Structured Advantages of the Integration 1. **Enhanced Data Discoverability**: With a unified metadata layer, data engineers and scientists can quickly locate and access relevant datasets, significantly reducing the time spent on data discovery. 2. **Improved Collaboration**: The synchronization of metadata fosters better collaboration between technical teams using SageMaker and business teams utilizing Alation, reducing conflicts and misunderstandings. 3. **Consistent Governance**: A singular source of truth for metadata enables consistent governance policies, which is crucial for compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining data integrity. 4. **Traceability and Auditability**: The integration ensures that all metadata updates include comprehensive provenance information, which supports audit trails necessary for compliance and data stewardship. 5. **Operational Efficiency**: By automating metadata extraction and synchronization, organizations can reduce manual efforts in metadata management, allowing data teams to focus on value-added activities such as analysis and insight generation. 6. **Security and Compliance Assurance**: The integration adheres to enterprise security practices by employing least-privilege access controls and encrypted communication, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected during synchronization processes. While these advantages are compelling, organizations must also consider potential limitations, such as the initial setup complexity and the need for ongoing governance to ensure metadata remains accurate and relevant. Future Implications of AI Developments As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, its integration within data engineering processes will likely deepen. Enhanced capabilities in AI are expected to automate data governance tasks further, including lineage tracking and anomaly detection in data quality. The future may also see the introduction of bi-directional synchronization capabilities, enabling metadata updates from either Alation or SageMaker, thus providing greater flexibility in managing data changes. This shift will empower organizations to adopt more agile and responsive data practices, aligning them with fast-paced business needs. In conclusion, the integration of Alation and Amazon SageMaker Unified Studio represents a significant advancement in unified metadata governance, positioning organizations to better navigate the complexities of data engineering while maximizing the value derived from their data assets. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context In the realm of applied machine learning, effective network traffic monitoring is crucial for maintaining system performance and security. As machine learning practitioners increasingly leverage cloud-based infrastructures and distributed systems, understanding network traffic becomes paramount. This knowledge allows for the optimization of data pipelines, detection of anomalies, and safeguarding against potential cyber threats. The command-line utility ‘iftop’ serves as a lightweight yet powerful tool for monitoring network traffic in Linux environments, providing real-time insights that can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of machine learning workflows. Main Goal and Achievement The primary objective of utilizing the ‘iftop’ command is to facilitate the monitoring of incoming and outgoing network traffic on a specified interface. This command enables users to visualize data flow in a clear and concise manner, thereby simplifying the management of network resources. To achieve this goal, practitioners simply need to install ‘iftop’ using their preferred package manager and execute it with the appropriate interface specified. This straightforward approach empowers users to keep track of network activity and identify any irregularities that may affect machine learning applications. Advantages of Using ‘iftop’ Simplicity and Efficiency: The ‘iftop’ command presents network data in an easily interpretable table format, allowing for rapid assessment of bandwidth usage without the complexities often associated with more comprehensive tools. Real-Time Monitoring: ‘iftop’ provides real-time insights into network traffic, enabling practitioners to make informed decisions promptly, which is critical for maintaining the performance of machine learning models operating in dynamic environments. Minimal Resource Consumption: Unlike heavier graphical interfaces, ‘iftop’ operates with minimal resource overhead, making it suitable for environments where computational resources are limited. Customizability: While ‘iftop’ offers various options for advanced users, its basic functionality is easily accessible, allowing users to adapt it to their specific monitoring needs without being overwhelmed by options. Security Insights: By monitoring outgoing traffic, practitioners can detect potential unauthorized data transmissions or telemetry, which is particularly significant in environments dealing with sensitive data. Caveats and Limitations Interface Dependency: ‘iftop’ requires users to specify the correct network interface to monitor. Failure to do so may lead to misleading data, as it defaults to the first available interface. Command-Line Proficiency: While ‘iftop’ is relatively simple to use, it still necessitates a basic understanding of command-line operations, which may pose a barrier for some users. Limited Historical Data: ‘iftop’ primarily focuses on real-time traffic and does not retain historical data, which may be a limitation for users needing long-term analysis. Future Implications As the landscape of machine learning continues to evolve, the integration of artificial intelligence into network monitoring tools is likely to enhance their capabilities significantly. Future advancements may include predictive analytics, enabling practitioners to forecast network traffic patterns and automatically adjust resources accordingly. Moreover, machine learning algorithms could be employed to identify anomalies in data flows, thereby increasing the efficacy of security measures against potential cyber threats. Overall, the intersection of machine learning and network traffic monitoring will become increasingly critical as organizations strive to optimize their data-driven initiatives. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context In recent years, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) has witnessed transformative advancements, particularly in image generation technologies. Among the most innovative tools in this domain is ComfyUI, an open-source, node-based interface that empowers creators and developers by providing extensive control over their creative workflows. Unlike traditional graphical interfaces, ComfyUI utilizes a modular framework that allows users to visually construct complex workflows without the need for coding expertise. This blog post aims to elucidate the core concepts of ComfyUI, its implications for Natural Language Understanding (NLU), and the benefits it offers to researchers and practitioners in this field. Main Goal and Achievement The primary objective of utilizing ComfyUI is to streamline the process of AI-powered image generation, enabling users—from novices to experts—to harness its capabilities effectively. This goal can be achieved through a comprehensive understanding of the node-based architecture, which facilitates the creation of intricate workflows tailored to individual needs. By familiarizing oneself with the various nodes and their functionalities, users can maximize the potential of ComfyUI to generate high-quality images and other multimedia outputs. Advantages of ComfyUI Visual Workflow Construction: ComfyUI’s node-based architecture allows users to create workflows visually, eliminating the need for programming skills. This democratization of technology enables a broader audience to engage with AI image generation. Customizability: The platform supports the use of custom nodes, allowing users to adapt the interface to meet specific project requirements. This flexibility fosters creativity and innovation. Cost Efficiency: As a free and open-source tool, ComfyUI eliminates the financial barriers associated with many commercial software solutions, making advanced image generation accessible to everyone. Local Execution: The ability to run ComfyUI locally not only enhances performance but also ensures data privacy, addressing concerns related to cloud computing. Scalability: ComfyUI supports various AI models, allowing users to select the most suitable one for their specific workflow, thereby optimizing output quality. Limitations and Caveats Despite its numerous advantages, ComfyUI is not without limitations. Users must possess a certain level of technical proficiency to navigate the platform effectively, especially when transitioning from cloud-based to local installations. Additionally, running ComfyUI locally necessitates robust hardware, particularly a capable GPU, which may not be available to all users. Lastly, while the open-source nature of ComfyUI promotes customization, there may be a steeper learning curve for those unfamiliar with such systems. Future Implications The continuous evolution of AI technologies, particularly in the realm of image generation, is poised to reshape the landscape of creative industries. As ComfyUI and similar platforms evolve, they will likely incorporate more sophisticated features, such as enhanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities, enabling users to generate more contextually relevant and high-quality outputs. Furthermore, the integration of AI tools into everyday workflows will empower Natural Language Understanding scientists to explore new methodologies for generating visual content, ultimately leading to richer, more immersive experiences across various fields, including education, advertising, and entertainment. Conclusion ComfyUI represents a significant advancement in the toolkit available to creators and developers interested in AI-powered image generation. Its node-based interface not only simplifies the creative process but also provides unparalleled flexibility and control. For Natural Language Understanding scientists, the implications of this technology are profound, offering new avenues for research and application in multimedia content generation. As AI continues to advance, platforms like ComfyUI will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of creativity and innovation. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Contextualizing Data Strategy in Resource-Constrained Environments In the realm of data analytics and insights, the development of a robust data strategy is paramount, particularly for organizations operating under financial constraints. The challenges faced by non-profit entities serve as a compelling case study for organizations, including those in the corporate sector, seeking to innovate while managing limited resources. Often, these organizations rely on basic tools and methods, such as spreadsheets, to manage complex datasets. This reality underscores a vital lesson: effective data practices do not require extensive budgets, but rather a clear purpose, trust among stakeholders, and a willingness to initiate change incrementally. Main Goal and Achieving It The primary objective articulated in the original content is to establish a data strategy that is contextualized and tailored to the specific needs of the organization, rather than adopting generic frameworks. This can be achieved by first identifying the key decisions that the data strategy should inform. By focusing on high-value questions and aligning data collection with organizational goals, entities can foster a culture of data-driven decision-making. This approach emphasizes purpose over technology, ensuring that data initiatives resonate with the actual needs of the organization and its stakeholders. Advantages of a Purpose-Driven Data Strategy Enhanced Decision-Making: Organizations that prioritize purpose in their data strategy often find that decision-making improves significantly. By identifying critical questions to address, data becomes a tool for meaningful insights, rather than mere compliance. Increased Engagement: When data initiatives are framed as tools to aid service users rather than administrative burdens, engagement from staff and stakeholders increases. This emotional investment can lead to higher participation rates in data collection efforts. Cost-Effectiveness: Organizations can achieve substantial outcomes using low-cost or free tools effectively designed to meet their needs. This approach encourages resourcefulness, as teams learn to maximize the utility of existing resources. Flexible Governance Models: A practical approach to data governance that avoids rigid compliance structures allows organizations to adapt quickly to changing circumstances while maintaining data integrity. Building Data Literacy: By fostering a culture of knowledge-sharing and mentorship, organizations can enhance overall data literacy, ensuring that data skills are not confined to a select few individuals. Caveats and Limitations While the advantages of a purpose-driven data strategy are evident, several limitations must be acknowledged. Resource constraints can lead to the risk of underinvestment in critical areas, such as data security and compliance. Moreover, the absence of dedicated data stewardship in smaller organizations can complicate governance issues, potentially putting sensitive information at risk. Lastly, the need for continuous engagement from all levels of staff is crucial; without this, even well-laid plans can falter. Future Implications and AI Developments As organizations navigate the evolving landscape of data analytics, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to significantly impact how data strategies are implemented. AI technologies offer the potential to automate data collection and analysis processes, reducing the manual burden on staff and enhancing the speed and accuracy of insights. However, the adoption of AI must be approached with caution, ensuring that ethical considerations, particularly around data privacy and bias, are prioritized. As the demand for sophisticated data capabilities increases, organizations must balance the allure of advanced technologies with the foundational elements of clarity and purpose that drive successful data strategies. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here
Context of AI Pilots and Production Realities The deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) in various sectors has garnered significant attention, particularly through the lens of pilot programs and proofs of concept (PoCs). These initiatives are designed to validate the feasibility of AI technologies, identify pertinent use cases, and foster confidence for larger-scale investments. However, it is crucial to recognize that these pilots often operate in environments that do not mirror real-world production scenarios. As such, they can create an illusion of success that may not translate into practical viability. As noted by Cristopher Kuehl, Chief Data Officer at Continent 8 Technologies, PoCs are conducted within a “safe bubble,” characterized by carefully curated data, limited integrations, and involvement from highly skilled teams. This insular approach can lead to structural misalignments, as highlighted by Gerry Murray, Research Director at IDC, who argues that many AI initiatives are predisposed to failure due to their foundational design flaws. Main Goal and Achievements in AI Deployment The primary objective of moving beyond pilot programs is to establish a sustainable and scalable AI implementation strategy that aligns with the complexities of real-world applications. Achieving this goal requires a paradigm shift towards composable and sovereign AI systems that prioritize adaptability, interoperability, and robustness. By focusing on these dimensions, organizations can enhance their capacity to deploy AI solutions that are not only effective in isolated environments but also resilient in diverse operational contexts. Advantages of Composable and Sovereign AI Enhanced Scalability: Composable AI allows organizations to build modular systems that can be easily expanded or modified according to evolving needs. This contrasts with traditional models that may be rigid and difficult to adapt. Improved Interoperability: Sovereign AI frameworks facilitate seamless integration across different platforms and technologies, thereby enhancing data flow and operational efficiency. Increased Resilience: By designing AI solutions that can function effectively in varied conditions, organizations mitigate the risk of failure associated with overly simplistic pilot programs. Real-World Relevance: A focus on practical application ensures that AI initiatives are grounded in the realities of the end-user environment, thereby increasing their likelihood of success. It is important to note, however, that transitioning to composable and sovereign AI systems is not without challenges. Organizations may face obstacles such as the need for expertise in new technologies, potential resistance to change within teams, and the complexity of integrating legacy systems. Future Implications for AI Research and Innovation As the field of AI continues to evolve, the implications of adopting composable and sovereign AI frameworks are profound. The future landscape will likely see a shift towards more collaborative and adaptable AI ecosystems that prioritize continuous improvement and user-centric design. This evolution will not only enhance the effectiveness of AI applications across various industries but will also democratize access to advanced technologies, enabling smaller organizations to leverage AI capabilities that were previously out of reach. In conclusion, the journey from pilot programs to fully operational AI systems demands a critical reevaluation of current practices and frameworks. By embracing composable and sovereign AI, organizations can pave the way for innovative solutions that meet the complexities of today’s dynamic environments, ultimately driving greater value and success in their AI initiatives. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here
Context In the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), human communication has always been a focal point for development. Just as humans learn to speak before they can read or write, the next significant evolution of AI interfaces is emerging: voice interaction. This transition is not merely a convenience; it is an alignment of technology with natural human communication patterns. In particular, the fields of Computer Vision and Image Processing stand to benefit from this evolution, as voice interfaces can enhance how specialists, such as Vision Scientists, interact with their tools and data. Main Goal and Achievement The central goal of integrating voice into AI systems revolves around creating a more intuitive and fluid interface that reflects human communication styles. This aim can be achieved by leveraging advanced speech recognition technologies and natural language processing capabilities. By aligning technological interfaces with human interaction paradigms, we can facilitate more natural and effective exchanges between humans and machines, ultimately leading to improved productivity and user satisfaction. Advantages of Voice Interaction in AI Natural Communication: Voice is the most instinctive form of communication, which allows users to engage more freely without the constraints of traditional input methods. This enhances productivity, particularly for Vision Scientists who often need to multitask. Reduced Cognitive Load: Voice interaction minimizes the need for backspacing and navigating complex menus, allowing users to focus more on their research and less on the interface. Accessibility: Voice interfaces provide significant benefits for users with disabilities or those who find typing difficult, ensuring that tools are usable for a broader audience. Real-time Interaction: Voice interactions are instantaneous and can seamlessly integrate into workflows, allowing Vision Scientists to query data or control systems without interrupting their focus. Contextual Understanding: Advanced AI systems equipped with voice capabilities can maintain context across conversations, enabling more meaningful interactions that enhance the quality of data analysis. Limitations and Caveats While the advantages of voice interaction are compelling, there are notable limitations. Voice recognition systems can struggle with accents, background noise, and overlapping speech, potentially leading to miscommunications. Additionally, users may have varying levels of comfort with voice technology, which can affect overall adoption and satisfaction. Future Implications The future of Computer Vision and Image Processing is poised for transformation as AI technology continues to advance. Enhanced voice interfaces will likely become more ubiquitous, providing Vision Scientists with sophisticated tools that are capable of understanding complex verbal instructions. As AI systems develop improved reasoning and contextual capabilities, the potential for real-time data manipulation and analysis through voice commands will expand significantly. This will not only streamline workflows but may also allow for more creative and exploratory approaches to visual data interpretation, fostering innovation in the field. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here











