
Context The introduction of the beta version of the Retrieval Embedding Benchmark (RTEB) marks a significant advancement in the evaluation of retrieval accuracy for embedding models within the realm of Generative AI. This new benchmark is particularly relevant as existing evaluation frameworks frequently fall short of accurately measuring true generalization capabilities of models, especially in real-world applications. The performance of various AI applications, including retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and recommendation systems, hinges on the quality of search and retrieval mechanisms. Consequently, developers face challenges in assessing how well their models will function in practical scenarios, making a reliable standard for evaluation crucial. Main Goal and Achievement Strategy The primary objective of RTEB is to establish a fair, transparent, and application-centric standard for evaluating the retrieval performance of embedding models on unseen data. This can be accomplished through a hybrid approach that combines both open and private datasets. By ensuring that evaluation metrics account for the generalization capabilities of models, RTEB aims to bridge the existing gap between reported performance on benchmark datasets and actual performance in real-world contexts. Advantages of the RTEB Framework Enhanced Generalization Assessment: RTEB addresses the generalization gap that exists in current benchmarks. By incorporating private datasets for evaluation, the framework mitigates the risk of models overfitting to training data, thereby providing a more accurate reflection of a model’s capabilities. Application-Focused Evaluation: The benchmark is designed with a focus on real-world domains, ensuring that the datasets used for evaluation are aligned with the needs of contemporary AI applications, such as law, healthcare, and finance. Multilingual and Domain-Specific Coverage: RTEB accommodates a wide range of languages and specific domains, thereby enhancing its applicability across various enterprise-level use cases. Transparency and Community Collaboration: The commitment to openness through public datasets fosters collaboration within the AI community. This transparency allows researchers and developers to reproduce results and suggest improvements, contributing to ongoing enhancements in retrieval evaluation standards. Focus on Robust Metrics: By prioritizing metrics like NDCG@10, RTEB offers a gold-standard measure for ranking search results, facilitating a more meaningful assessment of retrieval quality. Limitations While RTEB presents several advantages, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations: Benchmark Scope: The current focus is primarily on realistic, retrieval-first use cases, which may exclude more complex synthetic datasets that could further challenge model performance. Modality Constraints: At present, RTEB evaluates only text-based retrieval, with future expansions to multimodal retrieval tasks planned. Language Coverage Expansion: While RTEB includes datasets from multiple languages, ongoing efforts are required to enhance coverage for additional languages, particularly low-resource ones. QA Dataset Repurposing: Almost half of the datasets are repurposed from question-answering tasks, which could lead to lexical overlaps, favoring models that rely on keyword matching rather than genuine semantic understanding. Private Dataset Accessibility: The private datasets utilized for generalization testing are only accessible to MTEB maintainers, which could limit external validation and comparisons. Future Implications The establishment of RTEB as a community-trusted standard heralds a new era in retrieval evaluation. As AI technology continues to evolve, the ability to accurately assess model performance will become increasingly critical. Future advancements may lead to the integration of multimodal datasets and more diverse language representations, further enhancing the relevance of the benchmark. Moreover, as the AI landscape expands, the continuous involvement of community stakeholders will be vital in refining RTEB and ensuring it meets the emerging needs of developers and researchers alike. This collaborative approach will ultimately drive progress in the field of Generative AI, fostering the development of robust and generalizable models capable of meeting the complexities of real-world applications. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here
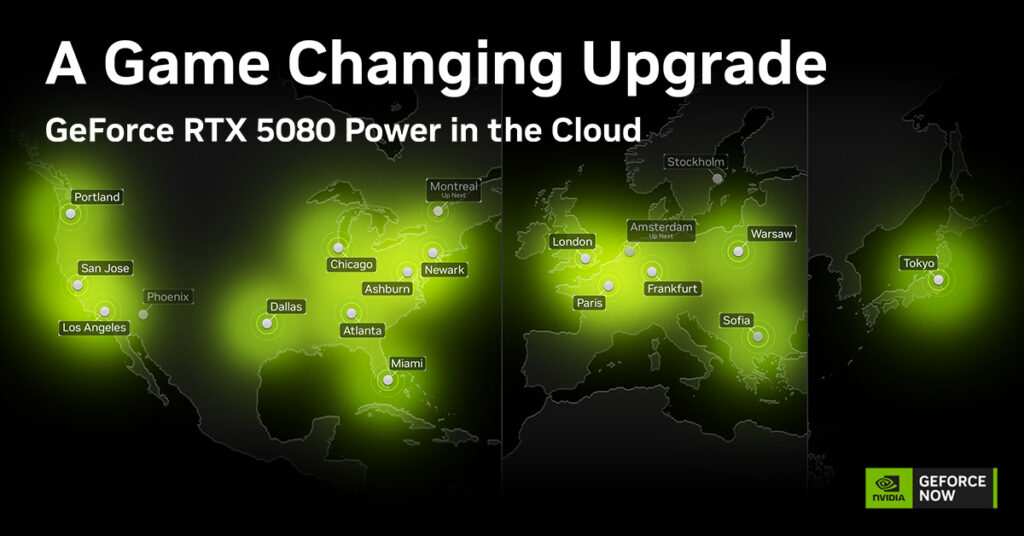
Contextual Framework: Cloud Gaming and Its Evolution The advent of cloud gaming has transformed how players engage with video games, and platforms like GeForce NOW exemplify this shift. As cloud technology continues to evolve, it enables gamers to access high-performance gaming experiences without the need for expensive hardware. This model is particularly relevant in the context of recent developments such as the launch of ARC Raiders, which is now available on GeForce NOW. This platform not only allows seamless access to new titles but also enhances gameplay through advanced graphics capabilities, including 5K resolution and real-time ray tracing. Main Objective and Its Achievement The primary goal highlighted in the original content centers around promoting the launch of ARC Raiders and encouraging gamers to adopt the GeForce NOW Ultimate membership. The strategy for achieving this objective involves offering incentives such as complimentary access to ARC Raiders with a 12-month Ultimate membership. This approach aims to expand the user base of GeForce NOW while enhancing the gaming experience through superior graphics and reduced latency. Advantages of Cloud Gaming with GeForce NOW Accessibility: Cloud gaming platforms like GeForce NOW democratize access to high-end gaming by allowing users to play on a variety of devices, including less powerful hardware. Performance: The integration of GeForce RTX 5080-class power provides gamers with cinematic visuals and smooth gameplay, significantly enhancing user experience. Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for expensive gaming consoles or PCs, cloud gaming offers a more affordable alternative for gamers. Instant Play: Users can immediately start playing new releases without the long wait times associated with downloads and installations. Continuous Updates: Since the games are hosted in the cloud, players benefit from automatic updates, ensuring they always have the latest versions without additional effort. Considerations and Limitations While cloud gaming offers numerous advantages, there are certain caveats to consider. For instance, users may experience latency issues depending on their internet connection quality. Furthermore, the reliance on cloud services raises concerns about data privacy and service reliability. These factors could potentially impact the overall gaming experience and should be carefully weighed by potential users. Future Implications of AI in Cloud Gaming The future of AI in the realm of cloud gaming is poised for significant advancements. As AI technologies continue to develop, they will likely enhance game design, player interaction, and server management. For instance, AI can tailor gaming experiences by analyzing user behavior and preferences, leading to personalized game recommendations and dynamic difficulty adjustments. Moreover, the integration of AI can improve network optimization, thereby reducing latency and enhancing overall gameplay. These developments will not only enrich user experience but also foster greater engagement within the gaming community. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context of Language Model Interpretability As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to evolve, the complexity of language models poses significant challenges in understanding their inner workings. The research area known as mechanistic interpretability seeks to illuminate these complexities, enabling researchers to gain insights into how these models function. In this context, Gemma Scope has emerged as a pivotal tool designed to enhance the interpretability of language models, specifically focused on the Gemma 2 family. By employing a suite of sparse autoencoders, Gemma Scope provides researchers with the ability to dissect and analyze the intricate mechanisms underlying language model behavior. Main Goal and Its Achievement The primary objective of Gemma Scope is to facilitate a deeper understanding of language models through the application of sparse autoencoders. These autoencoders serve as analytical tools that allow researchers to observe how language models process input and generate output. By leveraging these tools, researchers can identify and analyze various features that define the model’s operations. The achievement of this goal lies in the ability of the autoencoders to uncover the latent structures within a model’s activations without prior guidance on which features to investigate. This approach allows for the discovery of unexpected and potentially informative features, thereby advancing the field of AI interpretability. Advantages of Gemma Scope Enhanced Understanding: Gemma Scope allows for the dissection of complex language models, yielding insights into their operational features and behavior. Open Source Accessibility: By providing an open suite of sparse autoencoders, Gemma Scope democratizes access to advanced interpretability tools, fostering collaborative research. Robust Research Framework: The comprehensive nature of Gemma Scope supports ambitious research initiatives, potentially leading to the development of more robust AI systems. Protection Against Risks: Increased interpretability aids in building safeguards against model hallucinations and other unforeseen behaviors, enhancing AI safety. Scalable Techniques: The methodology employed in Gemma Scope can be applied to larger models, aiding researchers in tackling complex capabilities that emerge as models grow. Future Implications of AI Developments The advancements in AI interpretability herald significant implications for the future of the field. As AI models become increasingly sophisticated, the need for robust interpretability tools will intensify. The release of Gemma Scope signifies a move toward more transparent AI systems, which is essential for trust in AI applications. Future developments may focus on enhancing these tools to facilitate real-time interpretability, allowing for immediate insights into model behavior as it occurs. Furthermore, as AI technologies permeate various sectors, the ability to interpret and understand AI decision-making processes will be critical in addressing ethical, safety, and regulatory concerns. Thus, the evolution of tools like Gemma Scope will play a vital role in shaping the landscape of responsible AI deployment. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Introduction The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in the domain of large reasoning models (LRMs), has sparked a significant debate regarding their cognitive capabilities. Critics, such as those represented in Apple’s research article titled “The Illusion of Thinking,” argue that LRMs merely engage in pattern matching rather than genuine thought processes. This contention raises critical questions about the nature of thinking itself and whether LRMs can be classified as thinkers. This discussion aims to clarify these concepts and explore the implications for the field of Generative AI Models & Applications. Defining Thinking in the Context of LRMs To assess whether LRMs can think, we must first establish a definition of thinking. In this context, thinking pertains primarily to problem-solving abilities, which can be delineated into several cognitive processes. Key components of human thinking include: Problem Representation: Engaging the prefrontal and parietal lobes to break down problems into manageable parts. Mental Simulation: Utilizing auditory loops and visual imagery to manipulate concepts internally. Pattern Matching and Retrieval: Leveraging past experiences and stored knowledge to inform current problem-solving. Monitoring and Evaluation: Identifying errors and contradictions via the anterior cingulate cortex. Insight or Reframing: Shifting cognitive modes to generate new perspectives when faced with obstacles. Main Goal and Realization The primary goal of the discourse surrounding LRMs’ ability to think is to establish whether these models can engage in problem-solving that reflects cognitive processes akin to human reasoning. Achieving a consensus on this point requires rigorous examination of their performance on complex reasoning tasks and an understanding of the underlying mechanisms that facilitate their operations. Advantages of Recognizing Thinking in LRMs Recognizing that LRMs possess thinking-like capabilities offers several advantages: Enhanced Problem-Solving: LRMs have demonstrated the ability to solve logic-based questions, suggesting they can engage in reasoning processes that mirror human thought. Adaptability: By employing techniques such as chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, LRMs can navigate complex problems and adjust their approaches based on feedback from previous outputs. Knowledge Representation: The ability of LRMs to represent knowledge through next-token prediction means they can handle a wide array of abstract concepts and problem-solving scenarios. Performance Benchmarking: Evidence suggests that LRMs have achieved competitive performance on reasoning benchmarks, sometimes even surpassing average untrained humans. However, it is important to acknowledge limitations, such as the constraints of their training data and the absence of real-world feedback during their operational phases. Future Implications for AI Development The ongoing developments in AI and LRMs are poised to have profound implications for various sectors. As these models continue to evolve, their ability to process and reason through complex tasks will likely improve. This evolution could lead to: Increased Automation: Enhanced reasoning capabilities may allow LRMs to take on more sophisticated roles in problem-solving and decision-making processes across industries. Interdisciplinary Applications: The integration of LRMs into domains such as healthcare, finance, and education could revolutionize how data is analyzed and utilized, providing more nuanced insights and recommendations. Ethical Considerations: As AI systems become more capable of reasoning, ethical dilemmas surrounding their use will intensify, necessitating thoughtful governance and oversight. In summary, the exploration of LRMs’ cognitive capabilities not only enriches our understanding of artificial intelligence but also sets the stage for groundbreaking applications that could redefine problem-solving across multiple fields. Conclusion In light of the evidence presented, it is reasonable to conclude that LRMs exhibit characteristics of thought, particularly in their problem-solving capabilities. The similarities between biological reasoning and the operational framework of LRMs suggest that these models are not merely pattern-matching systems but rather sophisticated entities capable of engaging in complex reasoning processes. This realization opens the door for further exploration and application of LRMs in various domains, ultimately shaping the future of AI as a vital tool for problem resolution. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Contextual Overview Optical Character Recognition (OCR) has undergone significant advancements due to the emergence of powerful vision-language models (VLMs). These models have revolutionized document AI by offering capabilities that extend well beyond traditional OCR, enabling functionalities such as multimodal retrieval and document question answering. This transformation is particularly beneficial for Generative AI (GenAI) scientists, who are increasingly tasked with integrating sophisticated AI models into practical applications. The focus of this blog post is to elucidate how selecting open-weight models can enhance OCR pipelines while providing insights into the landscape of current models and their capabilities. Main Goal and Its Achievement The primary objective of the original post is to guide readers in choosing the appropriate OCR models tailored to their specific use cases. This goal can be realized through a systematic evaluation of the various models available, understanding the unique strengths of each, and determining when to fine-tune models versus utilizing them out-of-the-box. By following the structured approach outlined in the original content, readers can effectively navigate the complexities of contemporary OCR technologies and make informed decisions based on their needs. Advantages of Utilizing Open-Weight Models Cost Efficiency: Open-weight models generally offer more affordable options compared to proprietary models, particularly in large-scale applications where cost per page can accumulate rapidly. Privacy Considerations: Utilizing open models allows organizations to maintain greater control over their data, thereby mitigating privacy concerns associated with closed-source solutions. Flexibility and Customization: Open models enable users to fine-tune and adapt them according to specific tasks or datasets, enhancing their overall performance in targeted applications. Community Support and Resources: The open-source nature fosters a collaborative environment where users can share insights, improvements, and datasets, accelerating development and innovation in the field. Multimodal Capabilities: Many modern models extend beyond simple text extraction, allowing for the integration of various data types (e.g., images, tables) into a cohesive output, which is critical for comprehensive document understanding. Caveats and Limitations Despite the advantages, there are notable caveats associated with open-weight models. For instance, while they provide flexibility, the necessity for fine-tuning may require substantial expertise and resources, which could be a barrier for some organizations. Additionally, not all models possess the same level of performance across diverse document types, leading to potential discrepancies in accuracy. Furthermore, while community support is beneficial, it can also lead to fragmentation, making it challenging to identify the most effective solutions. Future Implications of AI Development in OCR The future of OCR technologies promises even more profound implications as AI continues to evolve. Advancements in VLMs are expected to lead to enhanced capabilities in understanding complex document layouts, improving the accuracy of data extraction from various formats, and offering real-time processing solutions. As the landscape of Generative AI expands, the integration of OCR with other AI applications will facilitate more robust document intelligence solutions, enabling organizations to harness data in unprecedented ways. Ultimately, ongoing research and development in this domain will likely result in models that are not only more powerful but also more accessible to a wider range of industries. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Contextual Overview The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare is revolutionizing access to medical services, particularly in underserved regions. One notable example is the deployment of AI-powered mobile clinics, such as the Women Cancer Screening Van in rural India, operated by the Health Within Reach Foundation. This initiative employs advanced AI technology from MedCognetics, a company based in Dallas, Texas. The van has successfully conducted breast cancer screenings for over 3,500 women, with 90% of the participants being first-time mammogram recipients. This innovative approach addresses the challenges of healthcare accessibility in developing countries, where traditional healthcare systems are often overwhelmed. Main Goal and Achievement Strategy The primary goal of this initiative is to enhance breast cancer screening accessibility for women in rural India, thus improving early detection rates and overall health outcomes. This objective can be achieved through the deployment of mobile clinics equipped with AI-driven diagnostic tools. By utilizing AI for rapid data triage and analysis, healthcare providers can identify high-risk patients and facilitate timely referrals for further evaluation and treatment. This model not only enhances the efficiency of screenings but also increases the likelihood of early cancer detection, significantly impacting survival rates. Advantages of AI-Powered Mobile Clinics Increased Screening Accessibility: The mobile clinic model brings screening services directly to rural communities, reducing travel barriers and associated costs for women who may otherwise forgo necessary medical care. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools: The integration of AI technology allows for rapid and accurate analysis of mammogram data, enabling healthcare professionals to identify abnormalities efficiently. Timely Referrals: The AI system can flag concerning results in real-time, ensuring that patients with abnormal findings are promptly referred to specialized medical facilities for further testing and treatment. Awareness and Education: Such initiatives raise awareness about breast cancer and the importance of regular screenings, potentially leading to increased participation in preventive healthcare programs. Data-Driven Insights: The collection and analysis of large datasets from screenings can inform public health strategies and improve resource allocation within healthcare systems. Limitations and Considerations While the benefits of AI-powered mobile clinics are substantial, certain limitations must be acknowledged. The reliance on technology may pose challenges in areas with limited internet connectivity, which could hinder real-time data sharing and analysis. Additionally, there is a need for ongoing training of healthcare personnel to effectively utilize advanced AI systems. Furthermore, cultural attitudes towards healthcare and potential stigma surrounding breast cancer may impact participation rates, necessitating tailored outreach strategies. Future Implications of AI in Healthcare The advancements in AI technology are poised to further transform healthcare delivery models, particularly in regions where access to quality medical services is limited. Future developments may include enhanced capabilities for on-site image analysis, allowing for immediate triage of patients in remote locations. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they may also incorporate predictive analytics, enabling healthcare providers to identify populations at higher risk for breast cancer and implement proactive measures. Ultimately, the continued integration of AI in healthcare has the potential to democratize access to essential medical services, significantly improving health outcomes for vulnerable populations. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Contextualizing the Misuse of Generative AI Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force across multiple domains, including creative industries, commerce, and public communication. However, the advancements in generative AI capabilities come with significant risks associated with misuse. This phenomenon encompasses a range of inappropriate activities, from manipulation and fraud to harassment and bullying. Recent research has highlighted the need for a comprehensive analysis of the misuse of multimodal generative AI technologies, aiming to inform the development of safer and more responsible AI applications. Main Goals of Addressing Generative AI Misuse The primary goal of the research into the misuse of generative AI is to identify and analyze various tactics employed by malicious actors utilizing these technologies. By categorizing misuse, the findings aim to inform governance frameworks and improve the safety measures surrounding AI systems. This objective can be achieved through systematic analysis of media reports, insights into misuse tactics, and the development of robust safeguards by organizations that deploy generative AI. Advantages of Understanding Generative AI Misuse Enhanced Awareness: By identifying key misuse tactics, stakeholders—including researchers, industry professionals, and policymakers—can develop a heightened awareness of potential risks associated with generative AI technologies. Informed Governance: The insights gained from analyzing misuse patterns can guide the formulation of comprehensive governance frameworks that ensure ethical and responsible deployment of AI. Improved Safeguards: Organizations can leverage research findings to reinforce their safety measures, thus minimizing the likelihood of misuse and enhancing user trust in generative AI applications. Proactive Education: By advocating for generative AI literacy programs, stakeholders can equip the public with the necessary skills to recognize and respond to AI misuse, fostering an informed society. Limitations and Caveats While the research offers valuable insights, it is essential to acknowledge certain limitations. The dataset analyzed primarily consists of media reports, which may not capture the full spectrum of misuse incidents. Furthermore, sensationalism in media coverage could skew public perception towards more extreme examples, potentially overlooking less visible but equally harmful misuse forms. Additionally, traditional content manipulation tactics continue to coexist with generative AI misuse, complicating the comparative analysis. Future Implications of AI Developments As generative AI technologies evolve, the landscape of potential misuse is likely to expand. Ongoing advancements in AI could lead to even more sophisticated exploitation tactics, necessitating continual updates to safety measures and governance frameworks. The integration of generative AI into various sectors raises ethical considerations, particularly around authenticity and transparency in AI-generated content. Future research and policy initiatives must focus on developing adaptive frameworks that can respond to emerging threats, ensuring the ethical use of generative AI while harnessing its creative potential. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Introduction In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, organizations face unprecedented challenges posed by machine-speed attacks. The collaboration between CrowdStrike and NVIDIA introduces an innovative approach that seeks to empower security operations centers (SOCs) with enhanced capabilities to counteract these threats through open-source artificial intelligence (AI). This partnership leverages advanced autonomous agents designed to transform the way enterprises defend against cyber adversaries, thereby shifting the balance of power in cybersecurity. Main Goal of the Collaboration The primary objective of the CrowdStrike and NVIDIA partnership is to equip security teams with autonomous agents that can proactively respond to threats at machine speed. This goal can be achieved by integrating CrowdStrike’s Charlotte AI with NVIDIA’s Nemotron models, allowing SOC leaders to transition from a defensive posture to a more aggressive stance against cyber-attacks. By employing open-source methodologies, the collaboration aims to enhance the transparency, efficiency, and scalability of AI applications in cybersecurity, ultimately reducing risks and improving threat detection accuracy. Advantages of the Partnership Enhanced Threat Detection: The collaboration allows for continual aggregation of telemetry data from CrowdStrike Falcon Complete analysts, enabling autonomous agents to learn and adapt based on real-world intelligence. This data-driven approach significantly enhances threat detection capabilities. Reduction of False Positives: By utilizing high-quality, human-annotated datasets, the partnership aims to minimize false positives in alert assessments. The Charlotte AI Detection Triage service has already demonstrated over 98% accuracy in automating alert assessments, which alleviates the burden on SOC teams. Scalability: The open-source nature of the technologies allows organizations to customize AI agents according to their specific security needs, making it easier to deploy solutions at scale across diverse environments. Transparency and Control: Open-source models provide enterprises with greater visibility into the operational mechanics of AI, enabling them to maintain data privacy and security. This is particularly crucial for organizations in regulated industries that require assurance regarding the integrity of their data. Proactive Defense Mechanisms: By bringing intelligence closer to data sources, the partnership promotes faster anomaly detection and response times, effectively addressing the speed of AI-driven attacks. Limitations and Caveats While the advantages of this collaboration are significant, certain limitations must be acknowledged. The complexity of integrating open-source AI into existing security frameworks may pose challenges for some organizations. Additionally, managing compliance and security throughout the lifecycle of open-source models requires diligent oversight and resource allocation. Furthermore, the reliance on high-quality data sources necessitates continuous updates and management of datasets to ensure optimal performance. Future Implications of AI Developments in Cybersecurity The advancements brought forth by the CrowdStrike and NVIDIA partnership suggest a transformative trajectory for cybersecurity practices. As AI technologies continue to evolve, the integration of generative AI models in security operations will likely become a standard practice. Future developments may include even more sophisticated algorithms capable of anticipating and neutralizing emerging threats in real-time. The emphasis on open-source solutions will not only enhance collaboration across the cybersecurity community but also foster innovation in defensive strategies, ultimately leading to a more resilient cybersecurity posture for organizations worldwide. Conclusion The collaboration between CrowdStrike and NVIDIA exemplifies a pivotal shift in the cybersecurity landscape. By harnessing the power of open-source AI, enterprises can effectively combat machine-speed attacks while maintaining control over their data. As the industry moves forward, the integration of these advanced AI technologies will be crucial in shaping the future of cybersecurity, ensuring that organizations are well-equipped to face evolving threats. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Introduction In the realm of Generative AI Models and Applications, the efficiency of data handling is paramount for researchers and developers. The challenges associated with loading extensive datasets, particularly those exceeding terabytes in size, can significantly hinder the training processes for machine learning models. The recent advancements in streaming datasets have introduced a paradigm shift, enabling users to engage with large-scale datasets swiftly and efficiently without the need for extensive local storage or complex setups. The innovations discussed herein aim to enhance performance while minimizing operational bottlenecks, fundamentally transforming the data ingestion landscape for AI practitioners. Main Goal and Achievements The primary objective of these enhancements is to facilitate immediate access to multi-terabyte datasets while minimizing the cumbersome processes traditionally associated with data downloading and management. By employing a straightforward command—load_dataset(‘dataset’, streaming=True)—users can initiate their training processes without the hindrances of disk space limitations or excessive request errors. This streamlined approach not only accelerates data availability but also ensures a robust and reliable training environment. Advantages Enhanced Efficiency: The improvements achieved 100x fewer startup requests, significantly reducing the latency associated with initial data resolution. Increased Speed: Data resolution times are now up to ten times faster, enabling quicker model training and iteration. Improved Throughput: The streaming capabilities have been optimized for twofold speed enhancements, facilitating smoother data processing during model training. Concurrent Worker Stability: The system supports up to 256 concurrent workers without crashes, promoting a stable and scalable training environment. Backward Compatibility: The enhancements maintain compatibility with previously established methods, allowing users to leverage improved performance without needing to modify existing codebases. Caveats and Limitations While the advancements present substantial benefits, several considerations should be acknowledged. The reliance on network stability and bandwidth can impact streaming efficiency. Additionally, while the system reduces request overhead, the initial setup and configuration may require technical expertise, particularly when optimizing parameters for specific hardware setups. Future Implications The implications of these developments extend beyond immediate performance improvements. As machine learning models continue to grow in complexity and dataset sizes increase, the need for effective data handling will become increasingly critical. Future enhancements may focus on integrating more sophisticated data management strategies, such as adaptive streaming protocols that dynamically adjust based on network conditions and model requirements. This evolution is likely to foster a more agile research environment, allowing AI scientists to innovate and deploy models more rapidly and efficiently. Conclusion In summary, the advancements in streaming datasets mark a significant milestone in the generative AI landscape, providing researchers and developers with potent tools to streamline their workflows. By addressing the challenges associated with large-scale data handling, these innovations pave the way for enhanced productivity and efficiency in model training, ultimately shaping the future of AI applications. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here
Context of AI Performance in Organizations Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly generative AI, have raised critical questions regarding the performance of data-driven organizations. A comprehensive survey conducted by MIT Technology Review Insights, encompassing responses from 800 senior data and technology executives, alongside in-depth interviews with 15 industry leaders, reveals a sobering reality. Despite the rapid advancements in AI technologies, many organizations find themselves struggling to enhance their data performance effectively. The research underscores a stagnation in organizational capabilities, reflecting a concerning trend for AI researchers and practitioners in the field. Main Goal of Enhancing Organizational Data Performance The primary goal articulated in the original report is to elevate data performance within organizations to meet the demands of modern AI applications. Achieving this objective is crucial for organizations seeking to leverage AI effectively for measurable business outcomes. To realize this goal, organizations must address several interrelated challenges, including the shortage of skilled talent, the need for fresh data access, and the complexities surrounding data security and lineage tracing. By addressing these issues, organizations can position themselves to capitalize on the full potential of AI technologies. Advantages of Enhancing Data and AI Performance 1. **Improved Data Strategy Implementation**: Despite only 12% of organizations identifying as “high achievers” in data performance, addressing the noted challenges can enhance strategic execution. A robust data strategy is foundational for effective AI deployment, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on accurate insights. 2. **Enhanced AI Deployment**: The report indicates that a mere 2% of organizations rate their AI performance highly, which suggests significant room for improvement. By focusing on data quality and accessibility, organizations can improve their AI systems’ scalability and effectiveness, transitioning from basic deployments to more integrated uses. 3. **Increased Competitive Advantage**: Organizations that successfully improve their data and AI capabilities are likely to gain a competitive edge in their respective markets. Enhanced data performance translates into better customer insights and more efficient operations, which are critical in today’s data-driven landscape. 4. **Operational Efficiency**: Streamlining data access and improving data management practices can lead to significant operational efficiencies. This not only reduces overhead costs but also accelerates time-to-market for AI-driven products and services. 5. **Future-Proofing Organizations**: As the AI landscape continues to evolve, organizations that invest in building robust data infrastructures are better positioned to adapt to future technological advancements. This proactive approach can mitigate risks associated with obsolescence and maintain relevance in an increasingly competitive environment. Caveats and Limitations While the potential advantages of improved data and AI performance are significant, certain limitations must be acknowledged. The persistent shortage of skilled talent remains a formidable barrier that cannot be overlooked. Additionally, organizations must navigate the complexities of data privacy and security, which can hinder the implementation of effective AI solutions. The findings also indicate that while organizations have made strides in deploying generative AI, only a small percentage have achieved widespread implementation, highlighting the need for continued investment in capabilities and training. Future Implications of AI Developments Looking ahead, the trajectory of AI development is likely to have profound implications for organizational data performance. As generative AI technology continues to mature, organizations that prioritize data quality and accessibility will be better equipped to harness its capabilities. Future advancements in AI are expected to further redefine the standards for data management, necessitating ongoing adaptation and innovation among organizations. In conclusion, the findings from the MIT Technology Review Insights report serve as a clarion call for organizations to reassess their data strategies in the context of AI. By addressing the identified challenges and leveraging the outlined advantages, organizations can not only enhance their operational performance but also secure a competitive edge in the evolving AI landscape. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here












