
Introduction The landscape of operating systems is evolving rapidly, particularly with the emergence of immutable Linux distributions designed for enhanced reliability and security. A notable example is ShaniOS, an Arch-based Linux distribution that promises to deliver a seamless user experience without the traditional vulnerabilities associated with system updates and configurations. This post aims to elucidate the significance of ShaniOS in the context of technology and its implications for software engineers and innovators in various fields. Main Goal of ShaniOS The primary objective of ShaniOS is to provide users with an immutable operating system that never breaks, thereby ensuring a reliable computing environment. This goal is achieved through a unique blue/green deployment strategy that allows users to seamlessly switch between two operational states of the system. By doing so, ShaniOS minimizes downtime and potential disruptions, making it an attractive option for both novice and experienced users alike. Advantages of ShaniOS Immutable Architecture: The core of ShaniOS is designed to remain unchanged, which significantly reduces the risk of system corruption due to errant updates or application installations. This robustness is crucial for environments where uptime is paramount. Blue/Green Deployment: Utilizing Btrfs subvolumes, the system maintains two simultaneous environments, enhancing the reliability of updates. Users can deploy updates to a passive environment, test them, and switch to it only when they are certain everything functions correctly, thus ensuring a fail-safe mechanism. Enhanced Security Features: ShaniOS incorporates stringent security measures such as AppArmor profiles, firewalled configurations, and full-disk encryption. These features protect against unauthorized access and potential data breaches, which is vital in today’s cybersecurity landscape. Application Management via Flatpak: The inclusion of Flatpak for application management allows users to install software in a sandboxed environment, further mitigating security risks. This is particularly beneficial for developers who need to manage dependencies and ensure compatibility across different environments. Performance Optimizations: ShaniOS is optimized for performance, with features like dynamic swap file creation and support for Nvidia GPUs. This ensures that users experience fast and efficient system operations, enhancing productivity. Limitations and Caveats While ShaniOS presents a range of advantages, it is essential to consider potential limitations. The reliance on a specific deployment strategy may require users to adapt their workflows, particularly those accustomed to conventional Linux distributions. Furthermore, the initial setup may be daunting for users unfamiliar with Linux environments. It is also crucial to note that, although the system is designed to be robust, no operating system is entirely impervious to issues, and users should maintain regular backups of their data. Future Implications of AI Developments As the fields of artificial intelligence and machine learning continue to evolve, the implications for operating systems like ShaniOS are profound. Future iterations could incorporate AI-driven monitoring tools that proactively manage system health, predict potential failures, and automate recovery processes. Additionally, AI could enhance security protocols, adapting to new threats in real time and providing users with a more secure computing environment. The integration of AI capabilities may also streamline application management, enabling more intuitive package installations and updates based on user behaviors and preferences. Conclusion ShaniOS represents a significant advancement in the realm of Linux distributions, particularly for users and developers seeking a stable and secure operating system. Its innovative blue/green deployment strategy, combined with robust security features and performance optimizations, positions it as a compelling choice for the modern computing landscape. As technology continues to evolve, particularly with the integration of AI, the potential for ShaniOS and similar distributions to adapt and thrive remains promising. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context and Overview The transformation of the Chinese agrochemical sector, particularly with the recent revisions to pesticide export regulations, represents a pivotal shift within the global agriculture landscape. The Department of Crop Production Management under China’s Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs has initiated new policies aimed at enhancing China’s competitiveness in the agrochemical market. These changes are not merely regulatory; they signal a broader shift towards innovation and global integration within the agricultural technology (AgriTech) and smart farming sectors. The implications of these developments extend beyond China, potentially reshaping agricultural practices and supply chains worldwide. Main Goals and Achievements The primary goal of China’s new pesticide policy is to facilitate the registration of pesticides intended solely for export, thus fostering innovation and enhancing global competitiveness among Chinese agrochemical firms. This is achieved through significant regulatory adjustments, including the introduction of export-only registrations, relaxed formulation restrictions, reduced toxicology data requirements, and expedited review processes. These advancements aim to streamline the entry of new products into international markets, enabling Chinese enterprises to leverage their existing reserves of active ingredients and formulation technologies effectively. By creating a more conducive environment for innovation, the policy encourages domestic companies to develop products that meet global standards and consumer demands. Advantages of the New Pesticide Policy Enhanced Global Competitiveness: The revised regulations allow for the registration of active ingredients not previously registered in China, enabling firms to introduce innovative products to international markets more quickly. Increased Export Volumes: Data from ICAMA indicates a robust increase in pesticide exports, with a 17.5% rise in volume and a 14% increase in export value in early 2025, showcasing the positive impact of the new regulations on trade. Boost to Innovation: By reducing bureaucratic hurdles related to toxicological data and registration timelines, companies are incentivized to invest in research and development, fostering a culture of innovation within the Chinese agrochemical sector. Market Responsiveness: The relaxed formulation ratios cater to diverse international market demands, allowing Chinese firms to produce customized solutions for various agricultural challenges faced globally. Caveats and Limitations While the new pesticide regulations present numerous advantages, several caveats must be acknowledged. First, there is a risk of insufficient market understanding among Chinese firms, particularly regarding pricing and channel management, which could hinder their competitiveness in sophisticated international markets. Additionally, the regulatory changes may not immediately translate to operational effectiveness, as companies must adapt their business models to align with the new export-driven strategies. Lastly, there remains a challenge in establishing mutual recognition of data between Chinese and OECD standards, which could impact the global acceptance of Chinese products. Future Implications and AI Developments As the agricultural landscape continues to evolve, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within AgriTech holds significant promise for the future. AI can enhance precision agriculture practices, optimize supply chains, and improve decision-making processes for farmers and agrochemical firms alike. With AI-driven insights, companies can better predict market trends, manage resources efficiently, and develop targeted marketing strategies that resonate with international audiences. Furthermore, AI can facilitate innovation by streamlining R&D processes, thereby accelerating the development of new agricultural solutions tailored to specific environmental and economic contexts. Conclusion The ongoing transformation of China’s pesticide policy is a harbinger of significant changes within the global agricultural sector. By fostering innovation and enhancing competitiveness, these regulatory reforms present a unique opportunity for AgriTech innovators to navigate and leverage the evolving landscape. As the industry adapts to these changes, the integration of AI technologies will further propel growth, ensuring that Chinese agrochemical companies can effectively compete on the global stage. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here
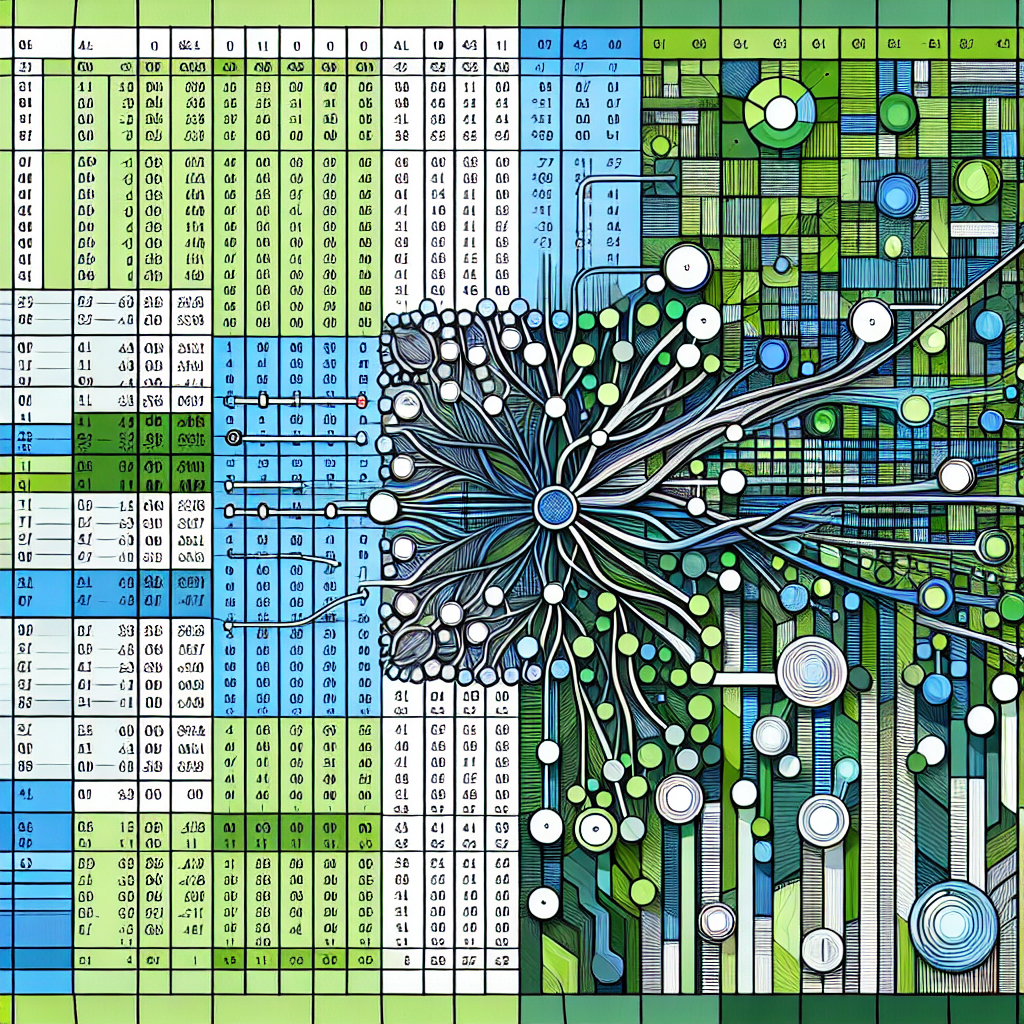
Introduction In the realm of machine learning, understanding the underlying mechanisms of algorithms, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), is paramount for practitioners aiming to leverage deep learning effectively. CNNs, often perceived as complex black boxes, offer profound insights into image recognition and classification tasks. This blog post seeks to elucidate the foundational principles of CNNs, illustrating their functionality through a straightforward implementation in Excel. By demystifying CNNs, we aim to enhance comprehension and foster practical skills among machine learning professionals. 1. The Representation of Images in Machine Learning 1.1 Detecting Objects: Two Distinct Approaches Object detection in images can be approached through two primary methodologies: deterministic rule-based systems and machine learning paradigms. The deterministic approach relies on manually encoded rules to identify features, such as defining a cat’s characteristics (e.g., round face, triangular ears). In contrast, the machine learning approach utilizes extensive datasets of labeled images, allowing the algorithm to learn defining features autonomously. This flexibility enables the system to adapt to various contexts, enhancing its predictive capabilities. 1.2 Understanding Image Structure An image is fundamentally a grid of pixels, where each pixel’s value corresponds to brightness levels ranging from black (0) to white (255). To facilitate understanding, this grid can be represented in a structured format, such as a table in Excel, aiding in visualizing how models process image data. For example, the MNIST dataset, which contains handwritten digits, can be reduced to a smaller grid for practical calculations without losing essential shape characteristics. 1.3 Classic Versus Deep Learning Approaches Before the advent of CNNs, traditional machine learning methods, including logistic regression and decision trees, were employed for image recognition tasks. Each pixel in an image was treated as an independent feature, which allowed for the identification of simple patterns with reasonable accuracy. However, this approach lacks the ability to account for spatial relationships among pixels, a significant limitation when dealing with complex images. 2. Constructing a CNN in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide 2.1 Simplifying CNN Architectures When discussing CNNs, it is common to encounter intricate architectures, such as VGG-16, characterized by multiple layers and parameters. To demystify these networks, we can begin with a simplified structure that employs a single hidden layer and larger filters, enhancing clarity in understanding the pattern detection process. 2.2 Designing Filters: A Manual Approach In practical scenarios, filters within CNNs are learned via training processes. However, to grasp their functionality, we can manually design filters based on known patterns, such as the average shapes of handwritten digits. This method emphasizes the interplay between human insight and machine learning, illustrating the foundational role of feature engineering in model design. 2.3 The Mechanism of Pattern Detection The core operation of a CNN is cross-correlation, which quantitatively assesses how well an image aligns with predefined filters. This process involves multiplying pixel values from the image and the filter, followed by summing the results to produce a similarity score. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for practitioners aiming to optimize CNN performance. 2.4 Implementing the CNN A structured implementation of a CNN in Excel involves defining the input matrix, creating filters, applying cross-correlation, and determining the predicted class based on the highest score. This practical exercise not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also equips practitioners with hands-on experience in model development. 2.5 Clarifying Terminology: Convolution vs. Cross-Correlation It is essential to distinguish between convolution and cross-correlation in CNNs. While convolution involves flipping filters, the operation typically performed in CNNs is cross-correlation. Understanding this distinction aids in clarifying terminologies commonly used in machine learning literature. 3. Advancements and Future Implications 3.1 Utilizing Smaller Filters for Detail Detection In advancing beyond the initial examples, employing smaller filters allows for the detection of intricate patterns within images. This approach enhances the model’s ability to recognize local features, which is pivotal in complex image recognition tasks. 3.2 Addressing Object Positioning One challenge in image recognition is managing the positioning of objects within images. By sliding filters across the image, CNNs can maintain robustness against variations in object placement, allowing for more generalized learning and improved accuracy. 3.3 Additional Components in CNNs CNNs often incorporate various layers and non-linear activation functions to enhance flexibility and robustness. Understanding the role of these components is vital for practitioners seeking to develop more sophisticated models capable of learning richer patterns. Conclusion Simulating a CNN within Excel provides an accessible and engaging method to grasp the fundamental principles of image recognition in machine learning. By demystifying the operations of CNNs through practical exercises, practitioners can enhance their understanding of deep learning and its applications in real-world scenarios. As the field of artificial intelligence continues to evolve, a solid comprehension of CNNs will be invaluable for professionals navigating the complexities of applied machine learning. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context In the pursuit of developing fair and responsible artificial intelligence (AI), measuring bias in machine learning models is of paramount importance. One key metric that has emerged in this context is the Bias Score, which serves as a framework for data scientists and AI engineers to identify and address hidden biases that often permeate language models. This metric is crucial for organizations striving to create equitable AI solutions, as it allows for early detection of biases that can adversely affect performance across diverse applications in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Understanding the Main Goal The primary objective of employing the Bias Score is to facilitate the development of AI systems that are not only effective but also equitable. Achieving this goal involves integrating the Bias Score into the model development lifecycle, enabling teams to proactively identify and mitigate biases in their AI systems. By recognizing these biases at early stages, organizations can enhance the fairness of their language models, increasing trust and reliability in AI applications. Advantages of Using Bias Score Quantitative Measurement: The Bias Score provides a numerical framework that allows for objective comparisons of bias levels across various models and datasets. This quantification aids teams in tracking improvements over time. Systematic Detection: Implementing the Bias Score enables the identification of biases that may be overlooked by human reviewers. Its structured approach captures subtle patterns that contribute to overall bias. Standardized Evaluation: The consistency of the Bias Score allows for comparative assessments across different AI models, supporting benchmarking efforts within the industry. Actionable Insights: The results derived from the Bias Score analysis provide clear indications of areas that require improvement, guiding specific strategies for bias mitigation. Regulatory Compliance: Utilizing the Bias Score can assist organizations in adhering to emerging AI regulations, demonstrating a commitment to ethical AI development. Enhanced Client Trust: Transparent reporting of bias metrics fosters confidence among clients and stakeholders, enhancing relationships through accountability. Caveats and Limitations Despite its advantages, the Bias Score is not without its limitations. Context sensitivity can lead to missed nuances that affect bias interpretation, especially in culturally diverse settings. Moreover, the effectiveness of the Bias Score is contingent upon the definitions of bias adopted by various stakeholders, which can lead to discrepancies in evaluation. Additionally, establishing appropriate benchmarks for what constitutes an unbiased model remains a challenge, as societal norms and perceptions of bias evolve over time. Future Implications The field of AI is continuously evolving, and the implications of developments in AI technologies are profound for bias measurement. As models become increasingly complex, the methodologies for bias detection, including the Bias Score, will need to adapt accordingly. Future advancements may see the integration of more sophisticated techniques that account for intersectionality and context sensitivity, enhancing the accuracy of bias assessments. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on ethical AI will likely drive organizations to prioritize fairness in their AI systems, reinforcing the role of metrics like the Bias Score in the development of responsible AI technologies. Conclusion In summary, the Bias Score serves as a critical tool for evaluating and mitigating bias in AI systems. By establishing a systematic approach to bias detection, organizations can foster greater equity in their AI solutions, leading to more reliable and inclusive technologies. As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, the importance of rigorous bias evaluation will only increase, underscoring the need for continuous improvement and adaptation in bias measurement practices. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here

Context and Relevance In the realm of software management, Microsoft has announced the emergency release of the Windows 10 KB5072653 out-of-band update. This measure aims to address persistent installation issues associated with the November extended security updates (ESUs). As Windows 10 reached its end of support on October 14, 2025, the absence of new features or free security updates necessitates alternative solutions for both individual users and business clients. To facilitate ongoing usage, Microsoft offers ESUs, which are critical for ensuring continued security and compliance for systems still operating on Windows 10. Primary Objective and Implementation The primary goal of the KB5072653 update is to rectify installation errors that users have faced while attempting to apply the November 2025 security updates. Organizations affected by these issues can implement the KB5072653 preparation package to resolve the 0x800f0922 errors encountered during the ESU update installation. Upon successful installation of this package, users are expected to seamlessly deploy the November security update, thereby enhancing the security posture of their Windows 10 environments. Advantages of the KB5072653 Update Enhanced Security: The installation of KB5072653 allows organizations to apply critical security updates, thus safeguarding their systems against vulnerabilities. Improved Compliance: By addressing installation errors, this update helps businesses maintain compliance with security standards and practices mandated within their industry. Cost-Effective Solution: Extended Security Updates provide a financially viable option for organizations reluctant to transition to newer operating systems. The cost for enterprise customers is structured to ensure access to necessary updates over a three-year period. User Convenience: The automated installation procedure enhances user experience, minimizing the need for extensive technical intervention. Limitations and Considerations Despite the advantages, there are caveats. Some corporate administrators have encountered issues with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), which may not accurately reflect the need for the ESU even when devices are properly enrolled. This inconsistency necessitates ongoing vigilance from IT teams to manually verify compliance and update statuses. Future Implications of AI Developments As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, its integration into software management processes, including patch management and update deployment, is anticipated. AI-driven analytics could enhance the identification of vulnerabilities and streamline update processes, thereby minimizing downtime and improving system resilience. Furthermore, predictive analytics could offer insights into potential issues before they arise, allowing organizations to proactively address challenges associated with software updates and system compliance. Disclaimer The content on this site is generated using AI technology that analyzes publicly available blog posts to extract and present key takeaways. We do not own, endorse, or claim intellectual property rights to the original blog content. Full credit is given to original authors and sources where applicable. Our summaries are intended solely for informational and educational purposes, offering AI-generated insights in a condensed format. They are not meant to substitute or replicate the full context of the original material. If you are a content owner and wish to request changes or removal, please contact us directly. Source link : Click Here







